What is the difference between a DV SSL and OV SSL certificate? Compare features, price, validation procedures, encryption, usage, and trust logos
SSL certificates can be divided in three types as per their validation levels: domain validation (DV), organization validation (OV) and extended validation (EV). In this article, we’ll discuss DV SSL vs OV SSL certificate to help you to choose the right SSL certificate for your website.
Before we move ahead, let’s cover the basics.
There are main two components of an SSL certificate’s utility.
- Encryption: An SSL certificate facilitates the encryption of data that’s transferred between website visitors’ browsers (the client) and the website (your server). This helps to prevent hackers and eavesdroppers from reading, interpreting, and misusing your clients’ data.
- Authentication: An SSL certificate authority (CA) also makes sure the data is received only by the intended receiver/website. This is done by asserting identity to authenticate the server.
Now let’s understand the main differences between DV SSL and OV SSL certificates.
Want to Compare DV SSL and OV SSL? Let’s Break Down the Differences
Encryption Level
All the SSL certificates are using the same SHA-256-bit hashing algorithm and 2048-bit RSA signature key. The CA/B Forum regulates the encryption standards. All the certificate authorities (CAs) have to comply with these rules, whether they’re providing a free SSL certificate or highly expensive one. All SSL certificates are equal as far as the first component, encryption, is concerned.
Validation Level and Authentication
Now here is where the actual difference between DV SSL and OV SSL lies. As we mentioned above, once the data is encrypted and transmitted successfully, only the intended receiver can decrypt it. So, it’s essential to verify who is at the receiving end. The CA verifies the identity of the website owner (which should be the company or individual who requested the certificate) before issuing the SSL certificate. This verification process distinguishes OV SSL certificates from DV SSL certificates.
DV SSL certificate: The CA will verify whether you own the domain for which you have applied for an SSL certificate. They send a verification email to a specific email address such as [email protected] or [email protected] with a verification link. Or, they may ask you to place some verification files on a particular location on your server. The validation process is automated, and the certificate can be issued within minutes.
OV SSL certificate: The CA verifies your company’s details such as its legal registered name, physical address, phone number, and email address by checking online government database. They might also ask for registration papers, professional opinion letters (POLs) or Dun & Bradstreet credit report. You must pass through basic steps involved in DV SSL certificates, too, to prove your domain ownership. The validation process is manually performed by the CA’s staff and can take one to three days.
A Brief History of Certificate Validation
Initially, all the SSL certificates were for single domains and offered organization validation. This means that only legitimate business organizations were eligible to get them.
However, with the rise of the internet, creating a website became way more accessible and inexpensive. But simultaneously, data theft incidents speared like wildfire too. So now, the need for encryption became a high priority.
To cover a large number of websites under the encryption’s umbrella, CA/B forum loosen up the validation standards. That’s how domain validated (DV) SSL certificates got introduced. If applicants could prove their domain ownership, they became eligible for encryption. That’s how small businesses, startups, freelancers, and personal website owners got the benefit of SSL encryption for their websites.
The Problem with Light Verification
The approach of giving more weightage to encryption than authentication has brought all the expected troubles. DV SSL certificates took away the power from CAs to verify whether the receiver of the information is a genuine business/person or a malicious character. That means that now anyone can get a DV SSL certificate and enjoy the benefit of encryption and a padlock security indicator — even for their malicious websites. According to APWG.org’s report, 58% of phishing websites are now using SSL/TLS certificate and have enabled HTTPS.
Usage
DV SSL certificates are suitable for personal websites, blogs, and informative websites that don’t handle or collect user information.
OV SSL certificates are recommended for any websites that take website visitors’ sensitive financial details or personally identifiable information (PII). These types of information include:
- Financial details: credit card/debit card numbers, SSN, tax details, bank account numbers, routing numbers, loan details etc.
- PII: names, physical address, phone number, email addresses and passwords, date of birth, etc.
All the medium to large businesses and reputed enterprises use OV SSL certificates as a minimum. Example: Facebook, Amazon, Twitter, Quora, etc.
Price
Commercial DV SSL certificates are available for a price as low as $12.42/year from RapidSSL with $10,000 warranty and attractive site seals.
You can get a free DV SSL certificate from some non-profits or hosting companies. However, you won’t get any warranty or site seal (TrustLogo) with a free SSL certificate. Another thing to keep in mind is to ensure the free SSL certificate you’re getting from a hosting site is not self signed. Some major browsers don’t trust self-signed SSL certificates and show a warning page with an “ERROR_SELF_SIGNED_CERT” error message.
There are no free OV SSL certificates available in the market. Well-known brands who sell commercial OV SSL certificates are Thawte, GeoTrust, Sectigo (formerly Comodo CA), Symantec, DigiCert, Entrust, GlobalSign and GoDaddy. OV SSL certificate starts from $77.61/year with $1,250,000 warranty and enhanced TrustLogo.
Site Seals
Most of the CAs offer static (non-clickable) site seals with DV SSL certificates and dynamic site seals with OV SSL certificate. Dynamic site seals are clickable and show live details about the certificate. i.e., issuance and expiry date, organization’s name, physical address, etc. It is the visual indicator of trust.
The Difference in Certificate Details
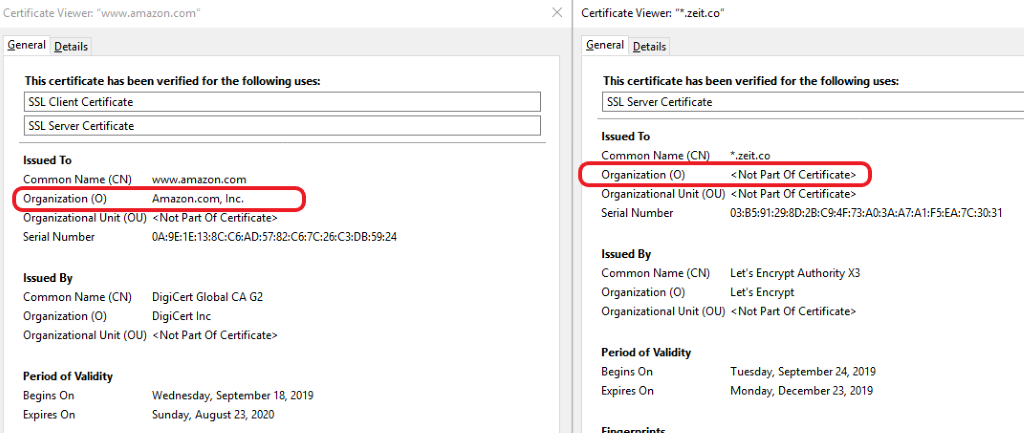

As you can see above, Amazon’s OV SSL certificate displays the organization’s legal operative name in the certificate details when a user clicks on the padlock sign in the browser. While the DV SSL certificate has not verified any details about the company, it doesn’t populate the organization’s name in the certificate.
DV SSL vs OV SSL Certificates: A Comparison Summary
| DV SSL Certificate | OV SSL Certificate | |
| Encryption Strength | 256 bits | 256 bits |
| RSA Signature Key | 2048 bits | 2048 bits |
| Validation Procedure | By clicking on validation link in the email or placing validation files on the server | By providing registration details, proof of physical address, phone number, etc. Sometimes professional opinion letters (POLs) or Dun & Bradstreet credit report is also required. |
| Validation Time | Within Minutes | 1-3 days |
| Usage | Personal websites, blogs, and informative websites | Websites that handle users’ financial data or personally identifiable information (PII). |
| Price | Starting from $12.42/year | Starting from $77.61/year |
| Free Options Available | Yes | No |
| Site seals | Static | Dynamic |
| Available in Wildcard and Multidomain SSL Types | Yes | Yes |
| Buy Now | Buy Now |





