Understand Online Vulnerabilities to Stay Secure for Android Devices
These days, “Mobile Vulnerabilities” and ‘Malware Attacks’ seem to be dominating the mobile threat landscape. Such threats have plagued the security scenario, more so in the case of Android devices. Often we hear about updates from the security industry pointing out new vulnerabilities found in Android OS, more sophisticated and hazardous than the previous version. Apparently, cyber-criminals are successfully finding intuitive ways to exploit this OS on these devices.
Mobile vulnerabilities are actually weaknesses found in the security of mobile devices and their operating systems. These vulnerabilities can potentially expose them to malware attacks and other malicious exploits, which really are just codes designed by hackers to specifically take advantage of the access to these devices and in turn use the device as they see fit for something small or for something on a larger scale.
Trojan.Droidpak: The New Kid on the Block
It is the newest entrant in the arena of mobile threats. Recently, security researchers have come across a Windows trojan called Trojan.Droidpak. It is skillfully designed to infect Android Devices that are connected to infected computers. Research experts at Symantec claim in their post that this is an apt example of sophisticated Windows malware specifically for Android Devices. Technical contributor & Symantec Security Spokesperson Flora Liu said “We’ve seen Android malware that attempts to infect Windows systems before, interestingly, we recently came across something that works the other way round: a Windows threat that attempts to infect Android devices”.
When this Trojan infects the computer, a malicious DLL file is dropped and registered as a system service by the threat. A configuration file is downloaded after that, which is analyzed later to retrieve a malicious Android PacKage (APK) file. In the next phase of the attack, Android Debug Bridge Tool is installed. This application is actually used to install malicious APK in the Android Devices attached to the infected computer via USB cable.
The process is repeated numerous number of times in order for it to be successful. It is to be noted however, that the process of infection is possible only if the USB debugging mode is enabled on that Android Smartphone. Nevertheless, once installed successfully, the Android threat poses as a Google App Store program [as shown in the figure below]
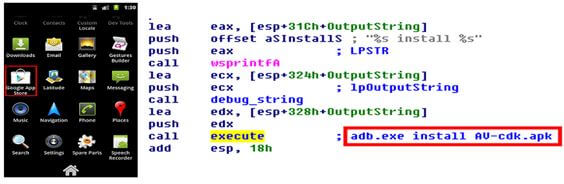
[Fig: Malicious Android App with Code Used to Install It]
The malware being installed by Droidpak is known as Android.Fakebank.B. This is actually a replica of a Korean online banking application. Interestingly enough, at the time of infection, if a genuine banking app is detected on the Android device by the malware, it is removed and replaced by the fake one. This malware is also highly capable of stealing login credentials and account information as well, when the Android user logs in using the replaced app. It is believed that Android.Fakebank.B also intercepts the text messages on that compromised device and sends them to cyber-criminals.
Important Security Tips for Android Devices
An Android Smartphone has almost become an integral part of our identity, which is exactly the reason why we should take extra efforts to ensure its safety for our own good. As we all know, Android Operating System is prone to quite a few malicious agents that can cause serious troubles right from being hacked to having compromised private data. Therefore, to avoid getting into such situations please follow these important tips:
Do Not Save Passwords: It is always best to avoid saving important passwords on your Android devices, especially in case of banking or payment applications. For anyone stealing private information from the device having saved passwords is a piece of cake.
Use in-built Security: From setting passwords and pins to creating patterns, in-built security offers many choices. Screen lock is like the fundamental step to maintain the privacy of the device and its contents.
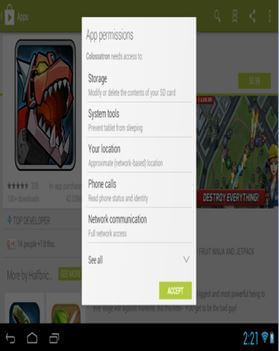
Use in-built Security: Carefully Read App permissions: In the haste of downloading and using the new app, many of us tend to ignore that little pop-up window that shows up right before downloading a new app from the Play Store. It is the list of the permissions required by the app. But it is very important to carefully read these permissions to make sure they correspond to what the application is all about. For example, a radio app doesn’t require permission to access text messages.
Download Original Apps from Authentic Developers: Apps from fake developers or pirated versions of apps tend to harbor malicious codes within them which can mess up with the content of the Android device. To avoid this, download ONLY the original app version from genuine developers.
Create a back-up of your Data: Creating a back-up of the valuable data stored in your android device is a must. In a worst case scenario, if the device gets infected or stolen, backed-up data helps you retrieve the original data.

Secure Network: Using a public Wi-Fi for online banking and shopping is not such a good idea as being in a public-shared network, attackers can easily sneak into your outgoing data.

Apps like Hideninja VPN can help you encrypt your outgoing. Also, a Wi-Fi protector can get help you get rid of these offenders. And if you have a rooted phone you can enhance security by applying settings from SecDroid.
Installing Anti-Virus: Our smart phones are our new computers, which is exactly why we need to treat them like one! And they rightly deserve the basic set of safety precautions like installing an Anti-Virus.
Encrypt Data: Data Encryption makes it tricky for cyber-thieves to extract the readable data from your device in case it’s lost or stolen. This can be enabled by Settings>> Security>> Enable Encryption
Updated Software in Phone: Updated operating systems minimize the hazards of security vulnerabilities. A lot of cyber-criminals depend on the lack of concern toward software update to run their malicious ventures.
A Few More Trojans to Watch Out For
Android smart phones by Google have taken the global smartphone market by storm. Within three years of being introduced to the world, Android has captured more than half of the market. Its rising popularity has also become the area of interest for all the malware writers because the percentage of Android malware is rising with each and every passing day.
Android’s open model serves as an ideal carrier for all the cyber-criminals who can inject Trojan Horses Malware hidden in software to make it look like an authentic application and then put them up on the open market for the users. Now, as the Users themselves download the apps due which the malware within the app easily bypasses Android’s strong built-in anti-virus protections.
Android devices’ vulnerabilities are giving enough reasons to the cyber-thieves for creating new varieties of malware, some of which posses the capability to gain root access on mobile devices and then install additional malware packages. Here are few strains of malware that every Android user needs to be aware of:
DroidDream: This was discovered in early March 2011. Detection of the DroidDream Trojan was significant, as it lay hidden in Google’s official Android Market. More than 50 different apps were found to be infected. The cyber-thugs picked the genuine apps, created by other software developers, added malware, and uploaded the infected app to the Android Market. DroidDream Trojan has an ability to collect information about SIM cards. This helps the cyber-crooks to clone more SIM cards, which are used to send premium-rate SMS messages, amount of which is credited in the user’s account.
DroidKungFu: Found in Chinese app market, this data-stealing Trojan exploits two vulnerabilities that enabled hackers to take total control of the Android device and steal the data within. Unlike DroidDream, DroidKungFu asks for less number of permissions when the user is downloading the app, to avoid suspicion.
Fakeneflic: This happens to be the malicious copy of the popular Netflix Android app. It was found to be highly capable to steal login credentials for real Netflix accounts. When the user logs in from an infected Android device into its Netflix account with the log in details, the system would crash and the Trojan would successfully steal the username and password.
GGTracker: This Trojan has an ability to get downloaded automatically to the device upon visiting a fake, malicious Android Market. It specifically targeted American users by signing them up for a number of premium SMS subscription without their consent. All the unapproved charges are pocketed by the hackers. Android users are directed toward this Trojan by clicking on an in-application advertisement about fake battery-saver etc.
Nickispy: Known for its ability to steal information about the location from infected Android devices using GPS or Wi-Fi network references, this Trojan is also good at recording phone calls and text messages and without approval send this private information to some remote site. Interesting fact related to Nickispy is that, some Chinese app stores openly marketed it as ‘adultery tracker’ to catch cheating spouses.
ZeuS: This notorious Trojan was nicknamed as ‘Banking Trojan’ as it intercepted online sessions between bank customers and their accounts.
It poses as a security application and seizes the one-time password that is texted to customers by the bank (which supposedly is the extra login security feature). Trojan ZeuS forwards that password to the cyber-criminals who can drain out customers’ bank accounts.
Anserver: Discovered by the security firm Trend Micro, Trojan Anserver can easily access information stored in user’s device. Not just that, it can also restart apps, make calls, send and receive text messages from the infected Android device.
It was found fixed in an e-book reader app available in a third-party Chinese Android app store. Anserver has an outstanding sophistication and it is proficiently designed to confuse researchers during the analysis by containing code obfuscation and signature verification. It also has the ability to detect and remove some anti-virus applications and collect commands from blog posts that are encrypted.
Foncy: Found by Kaspersky Lab, Trojan Foncy is an ‘SMS Trojan’, a common mobile malware. It was found embedded inside pirated versions of SuiConFo, a genuine Android app that monitors SMS and data usage.
Once installed, Foncy starts sending expensive text messages from the infected Android device profiting the cyber-criminals. It is noteworthy, that Foncy never targeted Russian or Chinese Android users. The victims happened to be users from Europe and Canada. Nevertheless, the list of target countries is surely growing.
The key for safe Android Usage is to tackle Android Vulnerabilities of the operating systems and follow safety tips to avoid malware attacks on the device.







 (5 votes, average: 3.40 out of 5, rated)
(5 votes, average: 3.40 out of 5, rated)

